A LEED Platinum home project overview
As building rating systems drive building codes to greater levels of performance, the rating systems themselves need a periodic upgrade to stay ahead of the curve; enter LEED version 4 (V4.) This latest version of the LEED rating system involved a comprehensive overhaul and to ensure relevancy and adoption LEED v4 was reviewed and broken down into positives and negatives by technical advisory groups.
When the Canada Green Building Council (CaGBC) anounced that the LEED for Homes rating system would raise the bar with the LEED V4 program, we at Ecohome were already mulling over the idea of building a showcase green performance home as a teaching tool, and decided to give the new LEED V4 a test drive.
We were already planning on building an ecologically responsible, super-efficient, passively-heated house, so we reckoned that much of the LEED program requirements would be happening anyway in this build. But it was interesting how the new LEED V4 approach involved more integrative processes.
This required all team members to be actively involved during the project, allowing them to work together to discover unique ways to reduce costs, material usage and to minimize the environmental impact of the home itself, and that of the occupants in living in the home in their habits, needs and lifestyle.
For example, one new aspect was to include a credit category for Location & Transportation, placing more emphasis and attention on reducing main contributors to global warming: transportation. The Location & Transportation category includes strategies to reduce costs, pollution and resource depletion related to daily commutes. So the Ecohome team decided early on to reduce the energy consumption of the home to a minimum while providing electric vehicle charging as an integral part of the energy use calculations.
We were pleased to get the confirmation that the Edelweiss House in Wakefield, QC received final certification of Platinum under the LEED V4 for Homes program, the first project and home in Canada to do so. Not only that, the Edelweiss House was only the second LEED V4 Platinum home certified worldwide - a result we are proud of and which prompted Thomas Mueller, President and CEO of the CaGBC to comment:
“The Edelweiss House is a phenomenal achievement - the first Canadian project to meet the stringent requirements of the latest version of LEED at its highest level, I commend Ecohome for being a leader in the Canadian home building community and for demonstrating to the industry that high sustainability standards can be achieved right here in Canada, right now.”
What is the cost of a LEED Platinum home?
The final Edelweiss 1552 sq.ft. house was built for only $300,000 Canadian in 2015, about $221,000 USD at current exchange rates), or $193 per sq. ft. (about $143 USD per sq.ft.) which is exceptional for such a high specification home. However this did include some unbilled time from the owner, who paid particular attention to such aspects as air sealing details which take time.
This build included a long list of environmentally friendly materials, specifically chosen to ensure a healthy internal air quality for the home, and includes mechanical systems with not one but three interwoven and efficient options for heating.
Some of the Eco-friendly features in the Edelweiss LEED V4 Platinum home (included in the build cost) :
- Low-flow plumbing fixtures that help the house use about 60% less water than a conventional home
- Zero-energy high performance septic waste-water treatment system
- Reclaimed and recycled materials, including a Silestone Cosentino Eco Line quartz countertop made with porcelain plates, bottles, and mirrors
- A wood ceiling made from reclaimed sunken river wood
- Environmentally friendly cork flooring
- Sandblasted antique interior doors
- Locally-sourced slate for bathroom floors and shower walls
- Lightweight synthetic gypsum drywall with high recycled content
- Mineral-wool insulation, including the insulation used under the slab
- LED lighting fixtures and bulbs
- Interior paints and floor adhesives with zero volatile organic compounds
- A DIY green living roof
- Under-slab high performance radon barrier
- Formaldehyde-free kitchen cabinets
- Split system air to air heat pump installation
- Air-to-water hybrid electric heat pump hot water heater
- High performance HRV ventilation system
- High efficiency ceiling fans for air circulation
- Triple-glazed argon filled wooden framed passive house standard windows
First performance benchmark for Edelweiss: Passive Solar Index 15
Registration date: August 25, 2015
Region: Outaouais, Quebec
Type of construction: Single-family New home
PSI rating: 15 kWh / m²
Method of calculation: measured post-occupancy
One of Edelweiss's most impressive attributes is its extremely low energy demands and operating costs. Energy-modeling software predicts that the house will use an average of 24.6kwh of electricity per day, or an average over the year of $1.39 (Canadian) per day based on current electricity rates from Quebec Hydro. For a full year, heating, cooling, and interior plug loads should add up to about $507 ($385 USD)
Even if the owners drove the 33 km to Ottawa every day for work in an electric vehicle, using the incorporated charging station at the house, that would bring total energy consumption to about $2.30 per day ($1.75 USD).
The Edelweiss House was designed and built by two founders of Ecohome, Emmanuel Cosgrove and Mike Reynolds, and as Reynolds puts it: "with some thought put towards costs savings in design, you don’t have to blow the bank to build a high-performance house. That’s what this project was really about, to show that super efficient homes can be built on a reasonable budget”.
First and foremost, Reynolds said, is the passive design of the house. “The primary heat source is the sun,” he said. “The majority of the heating requirement is met by the windows. So really, our primary heat source would be passive solar heat gain” .
The team also took advantage of deciduous trees on the south facing side of the building lot to effectively shield the windows from any possibility of overheating in summer, while allowing the lower winter sun to stream into the main living area and heat the thermal mass of the concrete floor. To ensure happy feet, there is also a hydronic radiant-floor heating system paired with an electric boiler with carefully controlled backup heating control system too.
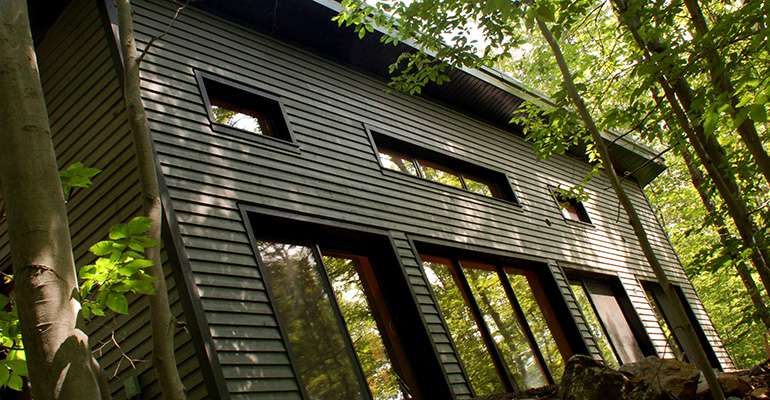
Exterior wall assemblies for this beautiful LEED platinum home include:
Insulation:
8 in. of semi-rigid mineral-wool insulation on the outside of the sheathing, and another 5-1/2 in. of mineral-wool batts in stud cavities packaged in a high-performance building envelope. Exterior walls of the slab-on-grade house have a total of 13-1/2 in. of mineral wool (5-1/2-in. batts followed by 8 in. of semi-rigid insulation) for a total R-value of 58. See here for full details of this LEED home's super-insulated wall design.
There is R-32 worth of mineral wool under the slab, and R-95 of mineral wool in the ceiling under the green roof.
Air sealing:
Edelweiss incorporated very careful attention to detail in air sealing the building envelope, and were able to achieve the very high Passive House airtightness standards.

Which renewable energy system was chosen?
Photovoltaic solar panel systems are often used to offset building energy requirements on high-performance or Net Zero Energy homes, especially as the cost of solar panels continues to fall. But for the LEED certified Edelweiss project, Ecohome didn’t think they would contribute sufficiently to offset their initial investment or the additional carbon footprint.
“You can get so much more if you invest first in efficiency,” says Reynolds. “There are a lot of houses that are going Net Zero Energy simply by popping on solar panels on top. But we wanted to bring it down to the basics and just show how little energy a house needs to use in the first place. Yes, we could have installed solar panels on top of it, but power in this region is all renewable hydro, not coal or another fossil fuels. so really the greenest power we could get was right from the hydro pole".
Why choose LEED Certification instead of Passive House?
Ecohome also decided for LEED certification instead of Passive House certification because even though the Edelweiss House’s energy consumption for heat and its level of airtightness are at or near the required levels. “We met the Passive House heat requirement and had virtually the same on air changes. Passive House is a great initiative, but the targets don’t reflect a Canadian climate on the whole, and LEED is a far more encompassing system that also includes the idea of a healthy home in it's choice of building materials".
Which is Canada's greenest home? Is it the Eidelweiss project?
With a heating requirement equal to that of Passive House, top points for energy efficiency of LEED V4 platinum, a slew of recycled materials, we'd like to think the Edelweiss House would be a main contender. But we acknowledge it's really hard to say; there are so many variables and criteria to consider.
Eidelweiss is a simply designed yet elegant Scandanavian feel, passively heated slab-on-grade rancher capable of housing a family of 4 comfortably in a sustainably sized home. And best of all, it was done well within a conventional building budget.
The premise of the Edelweiss House was to focus primarily on extreme performance, durability, healthy air quality and above all - affordability. Performance homes don't have to blow the budget and affordable houses don't have to be energy hogs. The energy savings in the Edelweiss house are so extreme that it would be considerably cheaper to buy and live in this house rather than a house built simply to meet the base requirements of building code - just about anywhere in North America.
The Edelweiss House is in Quebec, so it does benefit from lower than average power rates but then the climate is also potentially more extreme, so homeowners in other parts of North America should not immediately write-off the idea of heating a house like this with electricity based on high daytime rates.
As a house such as this requires very little heat to begin with, its passive heating by design and ability to retain heat by a combination of thermal mass and high performance insulation and building envelope design would make it very easy to limit any heating to off-peak hours if preferred.
“The biggest message we’re after is not to look at the building-code base requirement as a target to achieve and then just resign yourself to spending tons of money every month to pump heat into your house,” Reynolds said. “Instead, invest that in insulation and the payback is immediate. People tend to think the payback is going to be 20 years away, and it’s not. The payback starts when your neighbor turns on the heat and you don’t.”
For more information on this outstanding LEED Platinum V4 home and its construction, see the Ecohome Building Guide, or these pages:
Find more about green home construction and reap the benefits of a free Ecohome Network Membership here. |
If you would like to try a LEED Platinum V4 home before deciding to build one, and you'd like to visit this beautiful region of Quebec, then you can rent the Edelweiss LEED certified home here

|
|
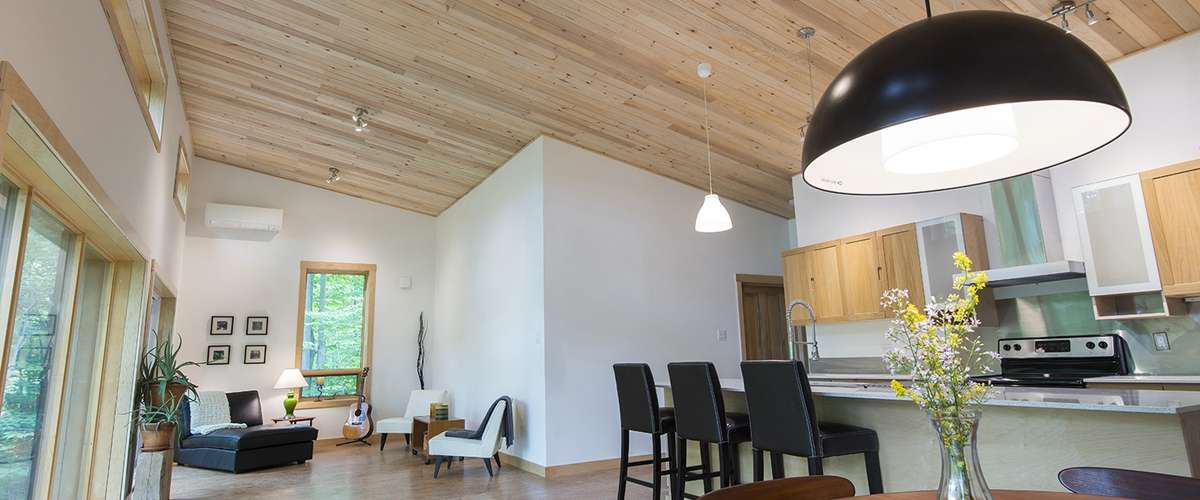
This LEED Platinum home is warm & inviting with cork floor, reclaimed wood ceiling & zero-VOC Kitchen © Ecohome
|

|
|
The reclaimed wood doors give the Edelweiss LEED platinum home extra points and some added charm © Ecohome
|

|
|
Rooms are flooded with light with carefully placed windows © Ecohome
|

|
|
Local slate was used for the bathroom floor & walls, as were low flow eco-friendly taps & toilet © Ecohome
|

































Very cool man! Is it occupied right now? Going to be very interesting to see how it performs in the real world after a few seasons of living in it. Love the design and layout.
The article on the CaGBC web site on this house indicates that it is heated by a hydronic radiant floor and an air source heat pump. Is the ASHP being used to heat the fluid in the radiant floor or is it used as a supplementary heat source? What manufacturer and model is being used for the ASHP and if its not being used to heat the radiant floor, what system is being used for that?
Hi August,
The heat pump is a ductless mini-split Mitsibushi Mr. Slim, and no, it does not heat the floor. Being a small and fairly open concept house with a low heat load, the Mr. Slim does most of the heating, and so the use of the radiant floor is quite limited, it's more about keeping the floor closer to the human body temperature for comfort rather than heat delivery. The boiler is powered by electricity, which in Quebec is renewable and quite affordable, but we still prefer to let the heat pump carry most of the load to keep consumption low.
Would you please direct me to a best products for ductless heating and cooling for the slab on concrete home ?
If you look at the top menu of Ecohome where is says 'find products', you can search 'slab on grade' and go to heat sources, or 'ductless ERV', you should be able to find what you are looking for in there. I am just not sure if you are referrering to heating and cooling the actual slab itslef. If so, you can find hydronic or air heated radiant floors, but cooling slab floors is not recommended either for comfort, or durabilty, in that a cold concrete floor would be a risk of developing condensation, mold and mildew. The most efficient way to heat a home though, would be with a heat pump.
Absolutely wonderful.
Can you tell what is the type of windows you use and what is the manufacturer?
Sure, no problem. The windows are wood-framed, triple-paned, argon filled with Low E coatings, we got them from Elilte Windows and Doors.
Do you have an old project bill of materials for your Edelweiss house? In 2021 I'm getting quoted $400-$900/sqft for a custom home, and one built to the energy/environmental specs of your design is closer to $900. Considering that's 6x the price, I'm curious about doing some comparative quotes for materials against your original project to see if things really are 6x as expensive now. (I'm aware that wood's twice the price lately as in 2019, but that's...still not 6x)
We don't have a materials list sorry.
That house is very simplistic in design, that helped a lot. One story slab on grade, cheap cork flooring rather than hardwood, single pitch roof so no angles or valley's or dormers, not a lot of corners, open concept indoor space without many division walls, reclaimed materials etc. If the house designs you are considering are more complicated, that would make a big impact on price.
Another big variable is that the housing market right now is insane. The price of buying a house, as well as the cost to build a new one are wildly unpredictable lately, and that is reflected in the prices builders charge. So it's impossible to compare at the moment, and remember we did that about 6 or 7 years ago. If you are talking to builders, the good ones at least are way over booked due to high demand, and prices do go up when that happens, that's just a reality of markets and supply and demand.
And our goal made the big difference I think - the premis of building that was to see if we could build one way better than code, for code prices, so we did whatever we had to to hit that target. It took some design sacrifices and some reclaimed materials to do it. When you go looking into modern house designs, they don't set out with the same mission as us, so the prices reflect that.
any possibility of pulling down a copy of your building plans? at a level that we could print in B size to submit for our area for local building permit. (our area is north Idaho and not California crazy). Thanks!!!
Are these available inn Canada or transferable to N.S. Canada