This is designed to offer only an overview of the 19 LEED for homes prerequisites that must be met for certification. Not all categories have prerequisites, and some have more than one. Please refer to the rating system for more details.
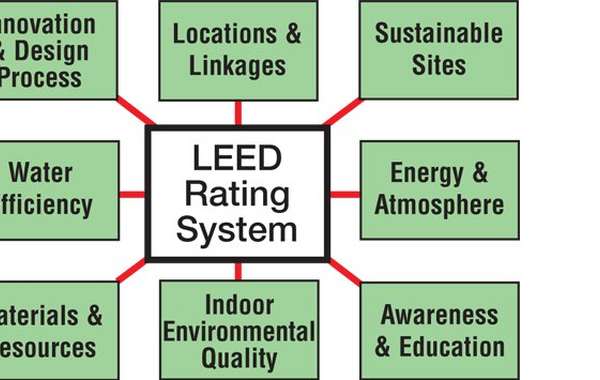
Innovation & Design Process (ID)
1.1 Preliminary rating:
Conduct a preliminary meeting with your LEED provider and key members of your project team. It is here where you will determine what points you are eligible for and wish to target, as well as the overall certification level you wish to achieve.
2.1 Durability planning:
Complete the Durability Risk Evaluation Form to identify all moderate and high-risk durability issues for the building enclosure.
2.2 Durability managemen t:
The builder must have a quality management process in place to ensure all durability measures have been successfully met.
Sustainable Sites (SS)
1.1 Erosion controls during construction:
Prior to construction, design and plan appropriate erosion control measures. The following measures must be implemented during the construction process.
- Stockpile and protect from erosion any disturbed topsoil for future use.
- Control the path and velocity of storm water runoff with silt fencing or comparable measures.
- Protect on-site storm sewer inlets, streams and lakes with straw bales, silt fencing, silt sacks, rock filters, or comparable measures.
- Provide swales to divert surface water from hillsides.
- If soils in sloped areas are disturbed during construction use tiers, erosion blankets, compost blankets, filter socks, or some comparable approach to prevent soil runoff.
2.1 No invasive plants:
Introduce no invasive plant species into the landscape. To find out more about invasive plant species, consult the Canadian Botanical Conservation Network.
Water Efficiency (WE)
3.1 Fixture efficiencies:
The only prerequisite in this category is that toilets do not consume more than 6.0 litres (or 1.6 gallons) per flush. Dual flush toilets meet these requirements and are easily found and affordably priced.
Energy & Atmosphere (EA)
1.1 Performance:
Your home must achieve a minimum energy performance rating of ERS (EnerGuide) 76 or HERS (Home Energy Rating System) 80. This will be determined during the compulsory energy rating blower door test.
11.1 Refrigerant charge test:
If your home has an air conditioning system with refrigerants, provide proof of a proper refrigerant charge of the system.
Materials & Resources (MR)
1.1 Framing order waste factor limit:
Limit the overall estimated waste factor of framing materials to 10% or less, and provide detailed documentation.
2.1 FSC-certified tropical woods:
Provide proof that any tropical woods found in the home are FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certified.
3.1 Construction waste management planning:
Investigate and document local options for diversion (e.g. recycling, reuse) of all anticipated major constituents of the project waste stream, including cardboard packaging and household recyclables (e.g., food and beverage containers).
Indoor Environmental Quality (EQ)
*Be sure to refer to the rating system guidelines regarding combustion appliances, venting requirements and ventilation systems.
2.1 Basic combustion venting measures:
Meet all of the following requirements:
- Ensure there are no unvented combustion appliances.
- Install carbon monoxide detectors on each floor.
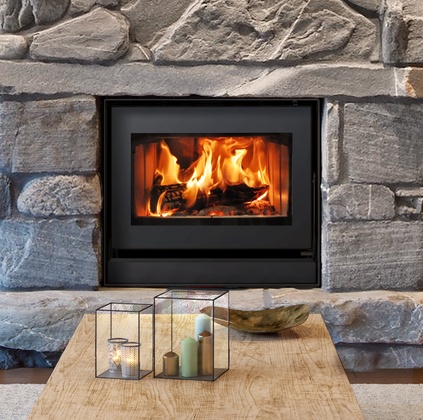
- Ensure all fireplaces, wood stoves and pellet stoves are either EPA-certified or meet the CSA B 415 standard. High performance masonry heaters and wood cook stoves are exempt.
- Combustion space and water heating equipment (such as natural gas) must be either closed combustion, have power-vented exhaust, be detached from the building, or located in an open air facility.
4.1 Basic outdoor air ventilation:
Homes must include a professionally approved passive or mechanical ventilation system.
5.1 Basic local exhaust:
Ensure proper venting of bathrooms and kitchens.
6.1 Room by room load calculations:
This is in regards to forced air systems, to ensure ducts are installed correctly and that they will provide the necessary air flow to all rooms. This is the job of the HVAC contractor, and an example of where an accountability form will need to be signed by the contractor ensuring proper steps have been taken.
7.1 Good filters
Forced air systems must have air filters with a minimum efficiency reporting value (MERV) ≥ 8 and ensure that air handlers can maintain an appropriate system pressure drop. Air filter housings must be airtight to prevent bypass or leakage.
9.1 Radon-resistant construction:
Homes in high-risk radon gas areas must have protection against radon infiltration. The project manager has the option to install a passive depressurization column (highly recommended) or to test for radon after construction is completed.
Installing a passive radon vent at the time of construction adds very little cost compared to additional measures required after project completion.
10.1 No HVAC in garage:
Place all air-handling equipment and ductwork outside of the fire-rated envelope of the garage.
Awareness & Education (AE)
1.1 Basic operations training:
Provide basic training for future occupants on the operation and maintenance systems and equipment. To satisfy this prerequisite, you must provide occupants with a manual on home operation systems and a minimum one-hour walkthrough.

































Comments (0)
Sign Up to Comment