Mold in homes is a bad sign so how to get rid of it or prevent mold in drywall?
Mold and mildew in homes develops in conditions of high humidity, most often in bathrooms, kitchens and basements, unless caused by roof leaks and other building envelope failures. Along with affecting the durability of your home, mold and mildew can cause or aggravate allergies, asthma and respiratory illnesses which means we should do everything possible to reduce mold growth.
Watch around the edge of bathtubs, showers and sinks for discoloration, and many basements finished or not can have a distinct musty smell that indicates a problem.

It’s important to determine the source of moisture so that the problem can be addressed. It can often be due to insufficient insulation resulting in condensation, improper vapour seals, or water in bathrooms and kitchens not being contained.
Along with proper design and keeping problem areas clean and dry, it is important to ensure bathroom fans, kitchen stove hoods and dryer vents are properly vented to the outside. If vents go up through your attic, be sure they aren't leaking, or more importantly that they aren't simply vented into the attic space, which does happen.
Basement mold & mildew prevention
That musty smell in basements that is all too familiar is due to either poorly installed insulation, or having no insulation at all. Building below grade presents much greater challenges than above grade as walls cannot dry to the outside. Please see our pages on how to prevent mold in basements guide and basement insulation guide guide to further understand this and work on a solution.
Dehumidifiers are a quick and easy solution to persistent humidity problems, it's a matter of a couple of hundred dollars to buy one and plug it in. Make sure to get one that is rated for the size of space you have, they aren't all the same.
You should also see this as an energy saving solution, not something that will cost you more money. A dehumidifier will cost maybe $10 or $15 a month to operate, but it will likely offer you more than that in savings as it takes less energy to heat and cool dry air than humid air.
If you have a mould problem, clean it with detergent. But mould will always come back unless you address the issue that caused it. See our pages on ventilation and air exchangers for more information on home humidity.
VOCs
Volatile organic compounds form a large part of household chemical pollutants. Formaldehyde, benzene, toluene, alcohols and mineral spirits are the most commonly found VOCs in our homes. They can cause many adverse health effects including dizziness, nausea, fatigue, respiratory illnesses, and cause damage to your kidneys, liver and nervous system.
VOCs are commonly found in furniture, kitchen and bathroom cabinets, paints, household products, drapes, carpets and electronics.
The Asthma Society of Canada says that the number of asthma cases being diagnosed world-wide increases by approximately 50% per decade. At present 3 million Canadians suffer from asthma, a rate that has seen a significant rise in the last 20 years.
Though researchers have yet to determine the exact cause of the increase in asthma rates, symptoms are brought on by chemical pollutants, air pollution, dust, pollen and pet dander. So it only makes sense that we pay attention to the air quality in our homes.
Where most people have heard the term VOCs is in regards to paint. There are many safer alternatives on the market now than the toxic paints we used to apply to our walls. For more information see our pages on safer paints, or you could even make your own DIY safe no VOC natural paint with our guide here.
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is one of the more commonly found contaminants in homes, and is used in the production of most particle board, plywood, furniture, drywall, and electronic equipment.

When new materials are introduced into a home, the odours that accompany them are quite noticeable at first. This can be anything from furniture, mattresses, cabinets, and even electronic devices like televisions and computers.
After a few days or weeks you may not notice the smell as much, but these contaminants can continue to be released for many years afterwards.
According to Health Canada, formaldehyde is a probable carcinogen over extended exposure. While no level is truly safe, at 30 ppb (parts per billion) children’s lung capacity will be affected, and homes showing formaldehyde rates of between 60 and 120ppb had higher rates of bronchitis and asthma among children. At around 100ppb most adults will begin to notice throat irritations.
New homes will often measure as much as 300ppb or more, over 10 times the amount that has been determined to be unsafe, and formaldehyde is only one of approximately 80,000 chemicals commonly found in household items.
There are non-toxic alternatives to many of the products we allow into our homes, that will facilitate much cleaner indoor air, and improved health. It's very difficult in the modern age to create a home free of contaminants while keeping the amenities we are accustomed too, but look at it as a cumulative effect. You will be exposed everywhere you go, so try to keep your home air as clean as you can.
One big-ticket item we would recommend taking extra time on choosing is the kitchen, in particular by specifying formaldehyde-free plywood for kitchen furniture - which is also available as formaldehyde-free and pre-finished UV cured VOC free plywood which really brings out all the beauty of wood without filling the air in our homes with noxious chemicals.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is often called the silent killer, as it is a colourless and odourless gas. Symptoms of exposure to high levels include headaches, nausea, fatigue, and disorientation. One of the reasons why it’s so dangerous is that people often think they’re sick, and instead of leaving the house, they go lie down, which can be fatal.

Carbon monoxide can find its way into your home by many means:
-
Gas or oil furnaces in poor condition
-
Unvented combustion appliances
-
Poorly maintained chimneys
-
Open fire placesLeaking wood stoves
-
Improperly sealed garages attached to homes
Make sure any combustible appliances are well maintained, install CO detectors on each floor of your house, and if possible avoid attached garages. If you have an attached garage, check to see that it is well sealed on the common wall with your house.
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs)
There is pretty much no escaping electromagnetic exposure in modern society, we are surrounded by it inside and outside our homes. Like so many other health concerns, it's just important to be aware of what the risks and concerns are so you can take the action you feel is necessary.
Whether or not EMFs are a health risk is continually being debated. In May of 2011 the World Health Organization recognized potential links between EMFs and cancer, but scientific research has shown no consensus either way.
Health Canada and the EPA has no guidelines for safe exposure, and while acknowledging potential links to cancer, their scientists have found no conclusive evidence and also point out that 'potential' links to cancer is a title that has been applied to many common substances.
This is meant neither to dismiss EMFs nor instill panic, but rather to tell you the issue is out there, and to help you make your own decisions. Humans have a long history of unknowingly exposing themselves to some pretty nasty things only to find out later how dangerous they are.
Some people believe they personally are strongly affected by EMFs and take significant steps to minimize exposure, including putting kill switches in all rooms to shut down currents running through walls.
If you are concerned, some simple actions you can take are:
-
Not putting clock radios right beside your head when you sleep.
-
Keeping your distance from active microwave ovens.
-
Shutting off wireless routers when not in use.
-
Limiting the length of cell phone calls.
-
Not purchasing a home directly under high voltage lines.
-
Keeping entertainment systems on a power bar you can easily shut off. There is a power draw through many appliances even when you are not using them. Many run warm even when not in use, and that ends up on your bill.
Levels of electromagnetism fall off exponentially over distance, so proximity is where the threat and solution would be. Whether you believe it to be a threat or not, a watched pot will never boil, so to be safe, don't press your face against the window of the microwave, it won't get you popcorn any sooner.
Flame retardants
Made from the chemical compounds chlorine or bromine, flame retardants have without a doubt saved lives by giving us valuable time to exit burning buildings, but those same chemicals are finding their way into our water, air and food chain.
Flame retardants are chemicals that have been added to home furnishings that slow the spread of fire. They can be found in almost all foam cushions of couches, beds, pillows, cars and baby strollers, as well as in electronic equipment like computers and television sets.
Due to health concerns there have been restrictions on brominated flame retardants (PBDEs), which has caused an increase in chlorinated flame retardants (CFRs), which may be safer but come with their own health risks, being a known carcinogen.
Health effects of PBDEs include links to reproductive disorders, complications during pregnancy and birth, behavioural development, attention deficit disorder and nervous system disorders.
Reducing your exposure:
Flame retardants will build up in household dust, so try to keep your home clean, and use a HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Arresting) vacuum filter. Avoid carpet under pads, and ensure that older foam cushions are well covered and not deteriorating.
While it is really not easy, you can try shopping for safer alternatives. They do exist, but you will probably have to do some leg work to find them.
Like so many other toxins, flame retardants build up in fatty tissue. Consequently, predators higher on the food chain can have dangerously high levels, which in some cases includes humans. Air and water currents moving north have led to alarmingly high levels of flame retardants in polar bears, as well as people living in northern communities.
Outside of household furnishings, to further reduce your exposure choose lean cuts of meat, low fat dairy products, and avoid farmed salmon, a notoriously high source of flame retardants.
Big fish eat little fish, and the toxins in the little fish move up the food chain.
See here for more information on keeping flame retardants out of your home.
Radon gas
Radon gas is a relatively unknown household danger. Of the people that have heard of it, not many realize the severity of health effects associated with it. Radon gas is released through the radioactive decay of uranium, and it is the radioactivity of it that makes it a danger to humans.
Health Canada estimates that radon gas is the cause of 10% of all lung cancer deaths, for a total of 2000 Canadian fatalities annually. Some of the highest levels in Canada are found in Ontario and West Quebec. The EPA in the USA also has a lot of information regarding the detrimental health effects of Radon Gas.

Radon enters homes through cracks in foundations, as well as from our water supply as it is aerated through showers and faucets. This is really only a problem for well water, most municipal systems come from lakes and rivers and have minimal levels.
For severe cases of radon in water there are solutions that can remove the gas, but they can be quite expensive. If you are in a high risk area and you don't have a proper radon vent, the amount in your water is probably negligible compared to the amount coming in through your basement, so your money might be better spent on sealing your foundation.
During new construction, a proper vapour barrier under your concrete floor and installing a radon vent will eliminate the problem for very little money. It's a simple matter of a 3 or 4 inch pipe with a T at the bottom underneath your slab, that is vented to the outside.
Kids and how poor air quality in the home can be dangerous for their health
To be clear, I'm not listing them as a pollutant, but rather the effects of pollutants on them.
Newborns and young children are particularly vulnerable to home pollutants as their lungs are still just developing. The first instinct when you are expecting a child is to start preparing your home for them, which inevitably includes new furniture. Clothes fresh out of the laundry and put into new cabinets will absorb formaldehyde as it off-gasses, which is not good for little lungs.
New baby clothes right off the rack will often contain many times the amount of formaldehyde that is deemed safe by the World Health Organization.
This is another reason for taking hand-me-downs or hitting the thrift stores. Used clothes that have been run through the wash a bunch of times will actually be much 'cleaner' than most brand new clothes.
Short of that, you can check labels and find suppliers that don’t use chemicals in production. You might spend a bit more, but they are relatively easy to find.
There are safer alternatives to a lot of the chemicals we introduce into our homes; it just takes a bit of research and buying from suppliers that are aware of these issues.
Now you know about maintaining healthy indoor air quality, learn more about sustainable construction for healthy and durable homes in the Ecohome Building Guide pagesFind more pages about sustainable and resilient green building techniques here :
Find more about green home construction in the Ecohome Green Building Guide pages - Also, learn more about the benefits of a free Ecohome Network Membership here. |
























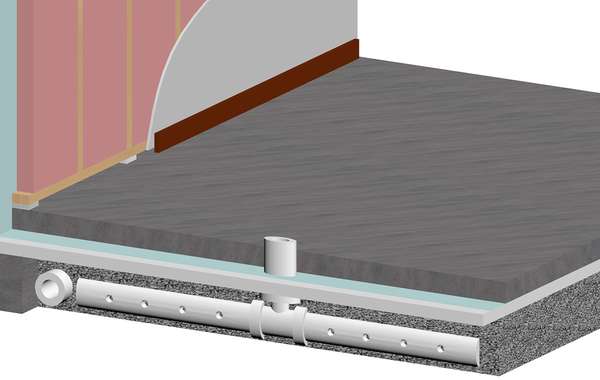




Very informative; love it!
Don't be tempted to buy any so called "permanent solution for poor indoor air-quality problems" the Ionic Paint Additive by Air-ReNu, which claims to be a blend of 27 natural rare-earth minerals that are ground into a fine powder then mixed with interior house paint. When applied to the walls of a room, the ionic additive cleans the air of any toxic impurities and odours, one treatment will maintain healthy indoor air quality for 8-10 years. I call complete BS on this one - show me some peer reviewed science before hawking it all over the internet!
Hi Mike,
Good article, but concerning EMFs, you imply Health Canada is trustworthy which it is not and that people are acting on beliefs and fear rather than facts.
In fact many countries such as Luxemburg, Switzerland, Nordic countries and even the Austrian Medical Association recommend precautionary measures to reduce EMFs, notably for the electrohypersensitive which account for 3-5% of the population
See Guideline of the Austrian Medical Association for the diagnosis and treatment of EMF related health problems and illnesses (EMF syndrome)
I'd add to your article:
install shielded BX cables in walls and floors surrounding beds, installing a demand switch to shut off voltage (source of electric fields) in bedrooms at night, unplugging wireless routers when not in use and cordless phones at night, having your home inspected to diagnose sources of significant EMFs including your electrical system if it is not properly grounded (not to mention safety and fire hazards), choosing a non communicating electric rather than a smart meter, keeping beds at least 2 meters away from the electrical main, and testing and mitigating sources of interference (so-called dirty electricity) etc.
Best regards
André Fauteux, Editor
La Maison du 21e siecle magazine
Thanks Andre,
I admire you for championing a cause you firmly believe in, but I would disagree with you that Health Canada is not a trusted resource for, ‘health’ issues. Alternatively, I would quote this from the World Health Organization – ‘’Based on a recent in-depth review of the scientific literature, the WHO concluded that current evidence does not confirm the existence of any health consequences from exposure to low level electromagnetic fields.’’
It is easy to find information on the web that will support or discredit any opinion, I find this topic to be no different. Many reliable sources seem to indicate that while it is not impossible that there are health effects, there is no firm evidence indicating there is a problem. So I don’t take a firm stance either way, If people want to go to the added effort and cost to limit their EMF exposure I support that, but I don’t think EMFs are something to instill panic about given that there are far greater, and proven, health issues in modern house construction that are left unaddressed. Example:
The toxins that can be found in standard building materials results in interior air quality that is many times worse than exterior air, so if it were me I would use whatever I could spare in a building budget to ensure I have no formaldehyde and VOCs in my home, as well as ensure my radon levels don’t exceed Health Canada’s recommendations.
Those threats to human health are not at all disputed and have been proven to cause respiratory diseases and cancer. So, to me it is a case of prioritizing.
And I am not claiming that it is certain there are no adverse health effects, because no credible body is making that claim, but I think you are fighting an uphill battle to stop EMF exposure in the modern age of electronics in which we live. Some of what you propose is pretty easy, but some is not. You propose installing infrastructure to shut off power in bedrooms at night and going around your home shutting off other sources, but what about the other 2/3rds of the day?
I would not like a router beside my bed, and thanks to you I shut off the wifi on my phone at night as I use it as an alarm like many people, but as I write this on my laptop I am thinking of all the exposure almost all of us are subject to - the phones in your pockets, the bluetooth in cars, wifi in workplaces, restaurants, coffee shops, and all the hours in your home when you are awake when all these EMF sources are operating. And anytime you stop and speak to another person, or even go for a walk in the woods, they may have a phone in thier pocket that you are exposed to. It's everywhere you go, so how do you mitigate that? You'd need to ditch your phone and computer and go live in the woods far from civilization. Best regards and respect to you for what you do!